LDES poised to outcompete lithium-ion batteries
Interest in long-duration energy storage (LDES) is rising rapidly as demand for clean firm capacity grows. With most LDES technologies still nascent, information about their cost is not widely available. In its inaugural LDES cost survey, BloombergNEF is bringing transparency to the matter.
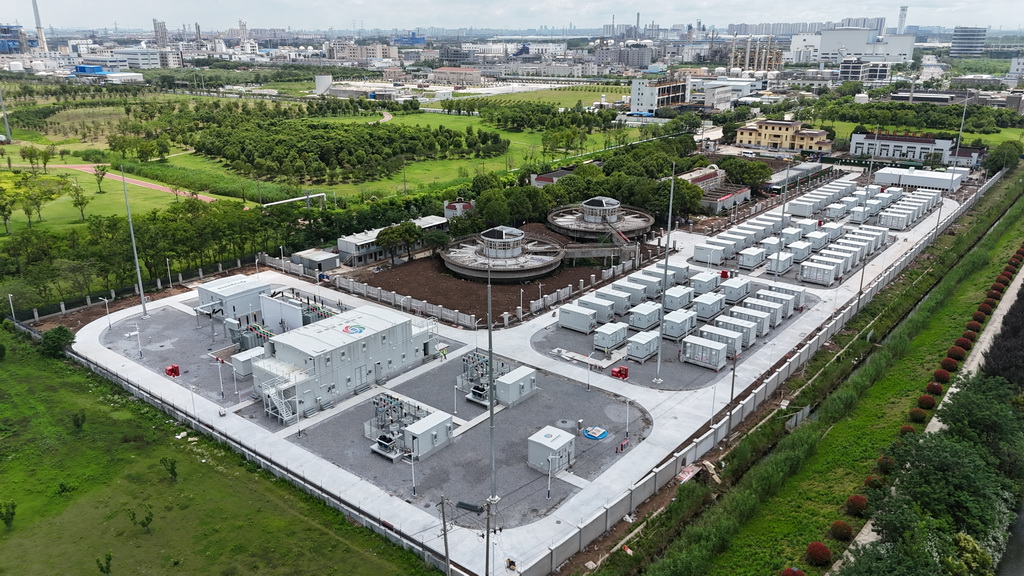
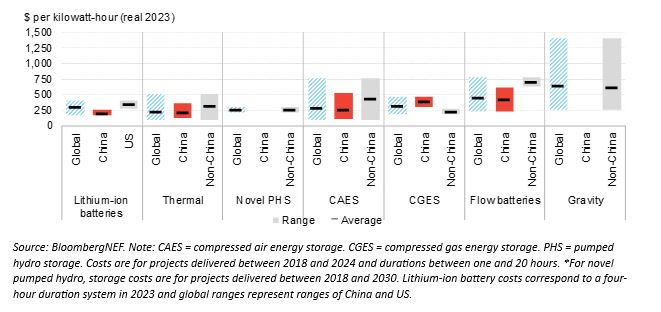
BNEF has surveyed seven LDES technology groups and 20 technology types in its report and found that the least expensive technologies are already providing cheaper storage than lithium-ion batteries for durations over eight hours.
Thermal energy storage and compressed air storage had an average capital expenditure, or capex, of $232/kWh and $293/kWh, respectively. For comparison, lithium-ion systems had an average capex of $304/kWh for four-hour duration systems in 2023, so generally shorter-term storage.
Storage duration, project size, and location are key factors affecting LDES capex. Gravity energy storage systems, which elevate weights when charging and controllably drop them when discharging, have the highest average capex, at $643/kWh.
The cost reduction rate of LDES technologies will largely depend on the expansion of deployment and the development of routes to market in major regions, BNEF notes. Thus far, flow batteries and compressed air technologies have had the most commercial success and could help ensure further cost reductions.
The demand for LDES is expected to grow in the future as the technology could help intermittent renewables act like baseload fossil fuel generators year-round. It is already being created through public procurement processess, such as the one launched in the Australian state of New South Wales this week.
However, LDES costs are unlikely to fall as fast as those of lithium-ion batteries this decade. This is primarily due to the fact that lithium-ion batteries are extensively used in both the transport and power sectors.
China vs. world
Presently, China leads the way on cost-effectiveness for established technologies like compressed air energy storage, flow batteries, and thermal energy storage.
The average capex in non-Chinese markets is 68% higher for compressed air storage, 66% higher for flow batteries, and 54% higher for thermal energy storage, BNEF finds.
“The significant cost disparity is largely due to China’s far greater adoption of LDES technologies,” says Yiyi Zhou, BloombergNEF’s Clean Energy Specialist. “While other nations are still in the early stages of commercializing LDES technologies, China is already developing gigawatt-hour scale projects, driven by favorable policies. This is particularly true for compressed-air energy storage and flow batteries, where China has set new project size records in the past two years. The rate of LDES installations in China is astounding.”
However, China is also producing lithium-ion batteries that are the cheapest in the world. Therefore, it may be more difficult for LDES to compete with the incumbent technology on the Chinese soil. According to BNEF, there are only a few LDES technologies, like natural cavern-based compressed air storage, that can outcompete lithium-ion batteries in terms of per-unit capital costs today.
Markets outside of China are developing a wider range of technologies compared to China.
LDES technologies have a better chance of competing with lithium-ion batteries in non-Chinese markets, where the lithium-ion batteries are more expensive. “While costs for LDES technologies outside of China are higher, the US and Europe have a chance to invest in their own industries and drive innovation and deployment,” says Evelina Stoikou, Energy Storage Senior Associate at BloombergNEF.
“Markets outside of China are developing a wider range of technologies compared to China, including more technology types within flow batteries, compressed air, compressed gas, thermal, gravity and novel pumped hydro. We’ve seen interest in those regions driven by ambitious clean energy targets, higher lithium-ion battery costs and an effort to develop alternative technologies that do not rely on lithium,” Stoikou says.