Global grid-scale BESS deployment up by 38% year-on-year through October
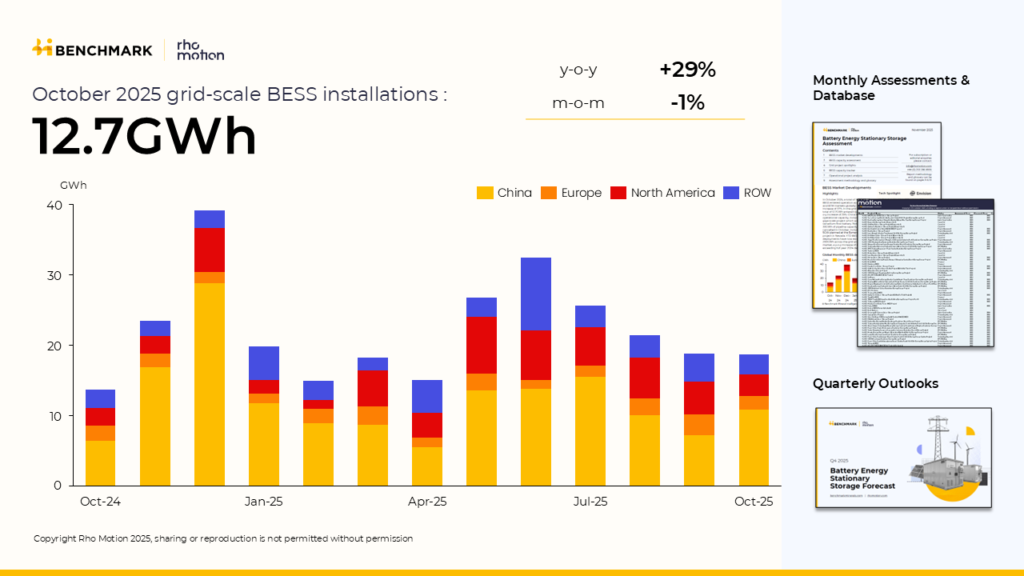
Global grid-connected battery energy storage system (BESS) installations have reached 156 GWh through October 2025, up 38% year-on-year compared with the same period in 2024, according to the latest data from Benchmark Mineral Intelligence’s Rho Motion.
China saw a 27% increase, while Europe and North America both recorded growth of 21%. Remarkably, the rest of the world (ROW) experienced a staggering 242% jump in deployments, highlighting a rapid acceleration of BESS adoption outside the traditional major markets.
In October, the global grid-scale BESS market added 12.7 GWh of new capacity, up 29% year-on-year. China led the gains, contributing just under 8.8 GWh of utility-scale BESS – a 72% increase from September – including one giga-scale vanadium flow battery.
The US posted the next-largest monthly additions with 2.3 GWh coming online. While this represents a 40% decline compared with September, it is 13% higher than October 2024.
Australia added 980 MWh of grid-scale BESS capacity with the second phase of the Waratah Super Battery in New South Wales. However, technical issues with transformer failures have temporarily limited its operating power to 350 MW until 2026.
In Europe, just under 500 MWh of new capacity was commissioned, including a 260 MWh project in Bulgaria, with Hithium serving as system integrator.
Project pipelines continued to expand, with just under 75 GWh proposed or announced in October 2025, marking a 5% month-on-month increase. Year-to-date, global pipeline additions have reached 732 GWh, up 23% compared with the same period in 2024, according to Rho Motion.
The largest project added this month was the Yan’an Wenergy Electricity Shaanbei-Anhui HVDC Project at 4.2 GWh. Another 16 giga-scale projects were announced, including 12 in Australia, which remains one of the world’s hottest energy storage markets.
More than 16 GWh of projects have assigned technology providers, and 32 GWh have entered construction globally. Notably, four projects of 1 GWh or more began construction in September, including Masdar’s massive 19 GWh project in Abu Dhabi. The Middle East is emerging as one of the fastest-growing regions for BESS installations in 2025, with construction timelines approaching the rapid pace seen in China.
However, over 30 GWh of pipeline capacity was cancelled in October, including more than 5 GW at the Esmerelda 7 Solar project in Nevada. Most cancellations occurred in China due to recent regional policy changes, Rho Motion says.
For the remainder of 2025, over 153 GWh remain in the pipeline and are scheduled to enter operation, though project delays and further cancellations are expected to reduce this figure by year-end.